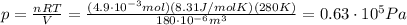We can solve the problem by using the ideal gas law, which states:
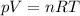
where
p is the gas pressure
V is the volume
n is the number of moles
R is the gas constant
T is the absolute temperature
The initial conditions of the gas in the problem are:
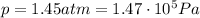
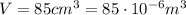
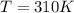
So we can use the previous equation to find the number of moles of the gas:
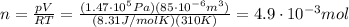
The final conditions of the gas are:
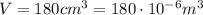
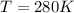
and since the number of moles didn't change, we can find the final pressure by using again the ideal gas law: