Answer:
The value of
 at 4224 K is 314.23.
at 4224 K is 314.23.
Step-by-step explanation:
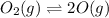
Initially
4.97 atm 0
At equilibrium
4.97 - p 2p
At initial stage, the partial pressure of oxygen gas = =4.97 atm
At equilibrium, the partial pressure of oxygen gas =
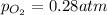
So, 4.97 - p = 0.28 atm
p = 4.69 atm
At equilibrium, the partial pressure of O gas =
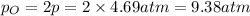
The expression of
 is given as :
is given as :
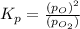
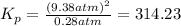
The value of
 at 4224 K is 314.23.
at 4224 K is 314.23.