Answer:
The probability of three codons will be 0.063 and the nonstop codons are ATT, ATC, ACT .
Explanation:
Given:
The genome content = 40%
To find:
Probability of three random consecutive nucleotide to form a stop codon.
Solution:
The Percentage of AT+ percentage of GC = 100.
The Percentage of AT = 100-40 = 60. [GC is given 40]
The Percentage of T = 30
=
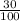
=
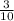
The Percentage of A = 30
=
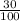
=
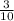
The percentage of G = 20
=
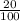
=
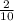
The percentage of C = 20;
=
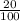
=
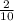
The nonstop codons are ATT, ATC, ACT
So, The probability of ATT
=
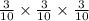
=
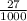
= 0.027
So, The probability of ATC
=
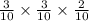
=
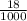
= 0.018
So, The probability of ACT
=
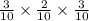
=
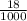
= 0.018
So, the answer is 0.027+0.018+0.018 = 0.063