Option A is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
Acceleration due to gravity
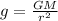
G = 6.67 × 10⁻¹¹ m² kg⁻¹ s⁻²
Let mass of earth be M and radius of earth be r.
We have
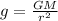
Now
A hypothetical planet has a mass of one-half that of the earth and a radius of twice that of the earth.
Mass of hypothetical planet, M' = M/2
Radius of hypothetical planet, r' = 2r
Substituting
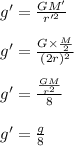
Option A is the correct answer.