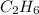Answer:
heat rejected =-1427820 KJ/mol of
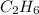
Step-by-step explanation:
Fuel ethane
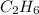
Burning Temperature = T =
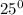
Pressure = P = 1 atm
The stiochiometric equation for this reaction is
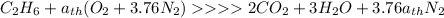
The enthalpy of the reaction is given as
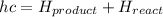
=
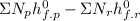
=
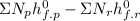

Where
N = number of poles
![h^(0) _(f) = enthalpy of formation at the standard reference state</p><p>From the enthalpy of formation tables at 25 degrees and 1 atm</p><p>Taking enathalpy of formation of [tex]CO_(2)]() = -393520 KJ/mol
= -393520 KJ/mol
Taking enathalpy of formation of
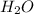 = -241820 KJ/mol
= -241820 KJ/mol
Taking enathalpy of formation of
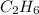 = -84680 KJ/mol
= -84680 KJ/mol

by putting values
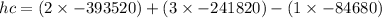
hc=-1427820 KJ/mol of
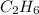
heat rejected = heat of enthalpy of formation
heat rejected =-1427820 KJ/mol of