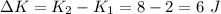Answer:
Case A:
Work-energy theorem states that the total work done on an object is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the object.
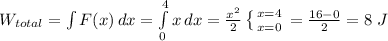
Case B:
In this case, we cannot calculate the total work done by
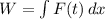 , because the force is a function of time, not position.
, because the force is a function of time, not position.
So, we need to calculate the initial and final kinetic energies.
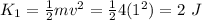
For the final kinetic energy, we need to find the final velocity. What we have is the force as a function of time. From Newton’s Second Law we can find the acceleration as a function time:
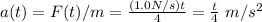
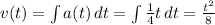
From this function, at t = 4.0 s, v = 2 m/s.
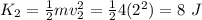
So, the change in the kinetic energy is