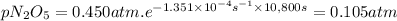Answer:
B. 0.105 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the following first-order reaction.
N₂O₅ → 2NO₂ + 1/2 O₂
We can find the pressure of N₂O₅ at a certain time t using the following expression.
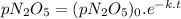
where,
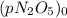 is the initial pressure
is the initial pressure
k is the rate constant
Given the half-life (t1/2), we can calculate k using the following expression.
k = ln 2 / t1/2 = ln 2 / 5130 s = 1.351 × 10⁻⁴ s⁻¹
When t = 3.00 h (10,800 s),