Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
M = Mass of Earth = 5.972 × 10²⁴ kg
G = Gravitational constant = 6.67 × 10⁻¹¹ m³/kgs²
r = Radius of Earth = 6371000 m
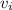 = Launch velocity = 14.8 km/s
= Launch velocity = 14.8 km/s
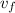 = Final velocity
= Final velocity
r = Orbit distance =
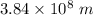
m = Mass of satellite
As the energy of the system is conserved we have
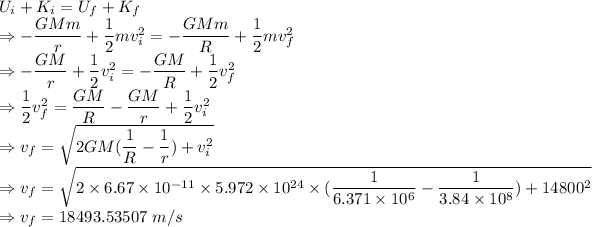
The meteroid's speed as it hits the earth is 18493.53507 m/s