Answer:
Option (b) is correct
Step-by-step explanation:
For a second order of reaction of type:
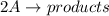
Rate law is -
![rate = k[A]^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/d48y2haoudb7nt6g30457ou0b3u1s27sb6.png) , where k is rate constant and [A] is concentration of A
, where k is rate constant and [A] is concentration of A
Integrated rate law is-
![(1)/([A])=(1)/([A]_(0))+kt](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/picnyedskobdbjerf7mnpnk88dpoohacvw.png) , where
, where
![[A]_(0)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qqxha3gkqyi6nvxca57jmthzzzu8zyjq3q.png) is initial concentration of reactant A and [A] is concentration of A after "t" time (k and [A]_{0}[/tex] are constants)
is initial concentration of reactant A and [A] is concentration of A after "t" time (k and [A]_{0}[/tex] are constants)
The integrated rate law can be compared with y= mx+c equation for a straight line (x vs y) where
![(1)/([A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2cs48or51s349n5qaz3s9yf29n256pa5ko.png) is y and t is x.
is y and t is x.
As the rate of reaction depends only upon concentration of X therefore-
![rate = k[X]^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/o6flkvxadloalm60q9h0nqylx26rixjkh4.png)