We will use the principle of overlap, specifically the principle of constructive interference to solve this problem. Mathematically this can be expressed as
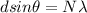
Where,
N = Number of fringes or number of repetition of the spectrum
d = Distance between slits
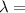 Wavelength
Wavelength
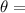 Diffraction angle
Diffraction angle
Our values are given as
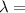 600nm
600nm

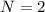
Replacing we have that the angle is,
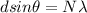
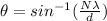
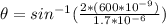
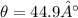
Therefore the second order line occurs at a diffraction angle of 44.9°