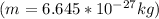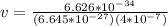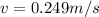To develop this problem we will use the DeBroglie relationship for which the wavelength is considered as
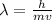
Where,
h = Planck's constant
m = mass
v = Velocity
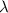 = Wavelength
= Wavelength
Rearranging the equation we have that the speed would be
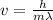
Our given values are considered
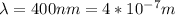

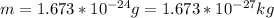
The value of the mass varies, therefore its speed would be given as:
Proton
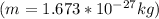
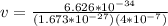
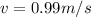
Neutron
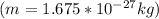
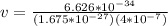
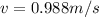
Electron
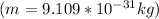
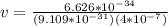
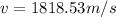
Alpha particle