Answer:
a)

b) As t →∞ y(t) becomes undefined as value of cos is undefined at ∞
Explanation:
Considering the complete question attached in fig below:
Non-homogeneous differential equation for given undamped system is:
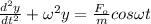 ---(1)
---(1)
To find general solution, consider the homogeneous part:
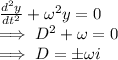
General solution is
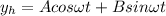
Using method of undetermined co-efficient,find the particular solution:
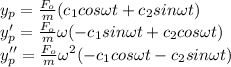
Substituting all these values in (1)
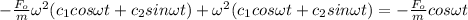
Equating the terms on both sides
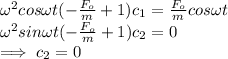
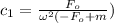
solution of given differential eq. :
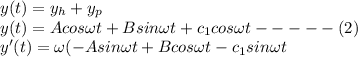
Using initial values :
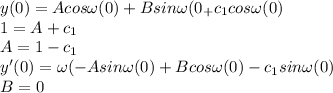
then (2) becomes
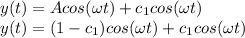

As t →∞
y(t) becomes undefined as value of cos is undefined at ∞