Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
mass of solute = 64.5 g, mass of solvent = 500 g = 0.5 kg (as 1 kg = 1000 g),
Temperature =
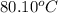 ,
,
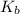 = 2.53 C/m
= 2.53 C/m
Also, we know that the relation between change in temperature, van't Hoff factor(i) and
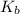 is as follows.
is as follows.
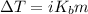
where, m = molality =
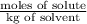
=
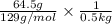
= 1
It is known that for non-electrolyte solute i = 1.
Hence, putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
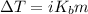
=
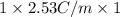
= 2.53 C
Therefore, calculate the boiling point of the solution as follows.
80.10 C + 2.53 C
= 82.63 C
Thus, we can conclude that the boiling point of the solution is 82.63 C.