Answer:
(a) Iron metal is oxidized, lead(II) cation is reduced;
(b) Silver cation is reduced, magnesium metal is oxidized;
(c) Copper(II) cation is reduced, magnesium metal is oxidized.
Step-by-step explanation:
The original question from ALEKS contains 3 reactions, we'll use them to illustrate the concept as well:
(a)
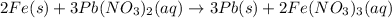 ;
;
(b)
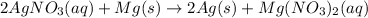 ;
;
(c)
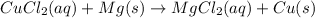
Using the abbreviation OILRIG, we know that oxidation is loss, reduction is gain (of electrons).
(a) We start with Fe at oxidation state of 0, as it's not bonded to anything and end up with iron(III) nitrate, iron has a charge of 3+ in this compound, as nitrate has a charge of 1- and 3 nitrate anions should be balanced by 3+:
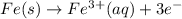
Iron metal loses 3 electrons, so it's oxidized.
Similarly, we start with lead with a charge of 2+ and end up with solid lead which is neutral:
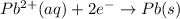
Lead(II) cation gains electrons, so it's reduced.
(b) Similarly, in this reaction we notice:
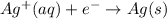
Silver cation gains an electron, it's reduced.
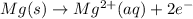
Magnesium metal is oxidized, as it loses electrons.
(c) Similarly:
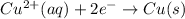
Copper(II) cation gains 2 electrons, so it's reduced.
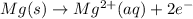
Magnesium metal loses 2 electrons, so it's oxidized.