The question is incomplete, here is the complete question:
Hydrosulfuric acid
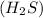 undergoes combustion to yield sulfur dioxide and water by the following reaction equation:
undergoes combustion to yield sulfur dioxide and water by the following reaction equation:
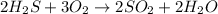
What is the
 of the reaction if 26.2 g of
of the reaction if 26.2 g of
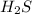 reacts with excess
reacts with excess
 to yield 431.8 kJ?
to yield 431.8 kJ?
Answer: The
 of the reaction is -1120.10 kJ
of the reaction is -1120.10 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
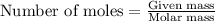
Given mass of hydrogen sulfide = 26.2 g
Molar mass of hydrogen sulfide = 34 g/mol
Putting values in above equation, we get:
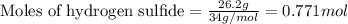
We are given:
Amount of heat released = 431.8 kJ
By Stoichiometry of the reaction:
When 0.771 moles of hydrogen sulfide is reacted, the amount of heat released is 431.8 kJ
So, when 2 moles of hydrogen sulfide will react, the amount of heat released will be =
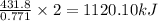
Sign convention of heat:
When heat is absorbed, the sign of heat is taken to be positive and when heat is released, the sign of heat is taken to be negative.
Hence, the
 of the reaction is -1120.10 kJ
of the reaction is -1120.10 kJ