Answer:
The electrophilic site that it will attack will be the carbonyl carbon
Step-by-step explanation:
Assuming that in the solution there is excess of carbonyl group attached compound
As ethoxide ion is a strong base, it can remove an acidic proton in an α-position to a carbonyl group
The resulting compound will be an enolate ion and in enolate ion the centre of attacking will be the carbon and as there is negative charge on the carbon, it will get stabilized because of resonance and - I effect of carbonyl group
As the negative charge on the carbon can be stabilized by resonance, it will be a weak base when compared to ethoxide ion but it has more nucleophilic character when compared to ethoxide ion because in polar solvents there will be solvation effect on ethoxide ion
The electrophilic site is the position where there will be partial positive charge and in this case the electrophilic site will be the carbon in carbonyl group attached compound because of - I effect of s
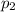 oxygen it will gain partial positive charge
oxygen it will gain partial positive charge