Answer:
17.78 m/s^2
Step-by-step explanation:
m = 0.5 kg
Weight on the planet, W = 20 N
Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of planet, g = W / m
g = 20 / 0.5 = 40 m/s^2
Radius of planet, r = 4 x 10^6 m
height, h = 2 x 10^6 m
Let the acceleration due to gravity at a height is g'.
According to the formula of acceleration due to gravity at height is
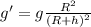
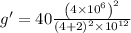
g' = 17.78 m/s^2
Thus, the acceleration due to gravity at height is 17.78 m/s^2 .