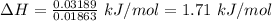Answer:
1.71 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The expression for the calculation of the enthalpy change of a process is shown below as:-
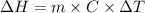
Where,
 is the enthalpy change
is the enthalpy change
m is the mass
C is the specific heat capacity
 is the temperature change
is the temperature change
Thus, given that:-
Mass of CaO = 1.045 g
Specific heat = 4.18 J/g°C
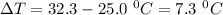
So,

Also, 1 J = 0.001 kJ
So,
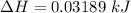
Also, Molar mass of CaO = 56.0774 g/mol
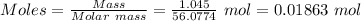
Thus, Enthalpy change in kJ/mol is:-