Answer:
a) 0.382
b) 0.021
Explanation:
We are given the following information in the question:
Mean, μ = 95 inches
Standard Deviation, σ = 0.5 inch
We are given that the distribution of lengths of lumber is a bell shaped distribution that is a normal distribution.
Formula:
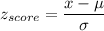
a) P( length greater than 95.15 inches)
P(x > 95.15)
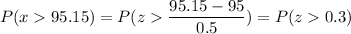
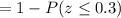
Calculation the value from standard normal z table, we have,
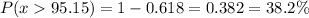
0.382 is the probability that a randomly selected board cut by the machine has a length greater than 95.15 inches.
b) Standard error due to sampling
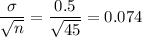
P( length greater than 95.15 inches in sample)
P(x > 95.15)
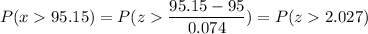
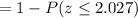
Calculation the value from standard normal z table, we have,
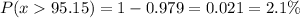
0.021 is the probability that their mean length of the sample is greater than 95.15 inches.