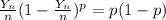Answer:
Explanation:
Let the random variable
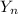 have a distribution thst id b(n, p)
have a distribution thst id b(n, p)
a)
![Pr[[(Y_n)/(n)-E[(Y_n)/(n)]\geq E]\leq(1)/(E^2)var[(Y_n)/(n)]\\\\=Pr[((Y_n)/(n)-P)\geq E]\leq (1)/(n^2E^2)np(1-p)=0](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/eyvabflakrgzs5cvcglo5bc7elv2mnxuz2.png)
Hence, it is obtained that
![(Y_n^P)/(n)=P</p><p></p><p>B)</p><p>As mentioned in a), use chebyshevs inequality.</p><p>[tex]Pr((Y_n)/(n)-E((Y_n)/(n))\geq E)\leq (1)/(E^2)var((Y_n)/(n))]()
![Pr[(1-(Y_n)/(n)-(1-p))\geq E]\leq (1)/(n^2E^2)np(1-p)=0](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/833hu45zys69o1rz8a9m2263y6kj5x79jo.png)
Hence, it is obtained that
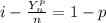
C)
As it was shown that
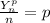 obtained the following
obtained the following
![[(Y_n)/(n)]^2^p=p^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/mathematics/college/xpnu3fqkktf7rrt0c0qbexezmxxga9w5ap.png)
Difference the above
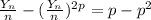
Hence the following expression has been obtained.