Answer:
Differential equation:
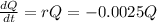
Solution of diff equation:
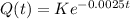
6.3% of the ozone in the atmosphere now will decay in the next 27 years.
Explanation:
The amount of ozone in the atmosphere may be found by the following differential equation:
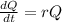
In which r is the constant of proportionality and Q is the amount of ozone. A positive value of r means that the amount of ozone in the atmosphere is going to increase, while a negative value means it is going to decrease.
Solving the differential equation:
We integrate both sides of the differential equation and apply the exponential function. So:
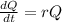
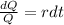
Integrating both sides
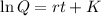
Applying the exponential:
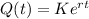
In which K is the initial amount of ozone.
So
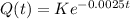
If this rate continues, approximately what percent of the ozone in the atmosphere now will decay in the next 27 years?
This K-Q(27).
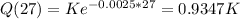
K - 0.9347K = 0.0653.
6.3% of the ozone in the atmosphere now will decay in the next 27 years.