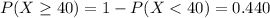Answer:
a)
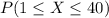
In order to find this probability we can use excel with the following code:
=GAMMA.DIST(40;5,8,TRUE)-GAMMA.DIST(1,5,8,TRUE)
And we got:
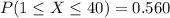
b)
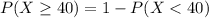
In order to find this probability we can use excel with the following code:
=1-GAMMA.DIST(40,5,8,TRUE)
And we got:
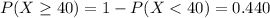
Explanation:
Previous concepts
The Gamma distribution "is a continuous, positive-only, unimodal distribution that encodes the time required for
 events to occur in a Poisson process with mean arrival time of
events to occur in a Poisson process with mean arrival time of
 "
"
Solution to the problem
Let X the random variable that represent the lifetime for transistors
For this case we have the mean and the variance given. And we have defined the mean and variance like this:
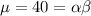 (1)
(1)
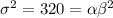 (2)
(2)
From this we can solve
 and [/tex]\beta[/tex]
and [/tex]\beta[/tex]
From the condition (1) we can solve for
 and we got:
and we got:
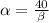 (3)
(3)
And if we replace condition (3) into (2) we got:
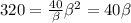
And solving for
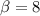
And now we can use condition (3) to find

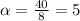
So then we have the parameters for the Gamma distribution. On this case
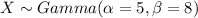
Part a
For this case we want this probability:
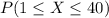
In order to find this probability we can use excel with the following code:
=GAMMA.DIST(40;5,8,TRUE)-GAMMA.DIST(1,5,8,TRUE)
And we got:
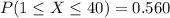
Part b
For this case we want this probability:
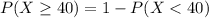
In order to find this probability we can use excel with the following code:
=1-GAMMA.DIST(40,5,8,TRUE)
And we got: