Answer:
(a). The magnitude of the average torque acting on the flywheel about its central axis during this period is 1.47 N-m.
(b). The angle that the flywheel does turn is 20.3 rad.
(c). The work done is -29.84 J.
(d). The average power of the flywheel is 19.89 W.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Rotational inertia = 0.140 kg m²
Initial angular momentum of flywheel = 3.00 kg m²/s
Final angular momentum of flywheel = 0.800 kg m²/s
Time = 1.50 sec
(a). We need to calculate the magnitude of the average torque acting on the flywheel about its central axis during this period
Using formula of torque
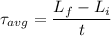
Put the value into the formula
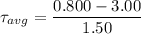
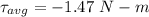
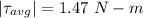
(b). Assuming a constant angular acceleration, through what angle does the flywheel turn
We need to calculate the angle that the flywheel does turn
Using equation for angle
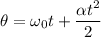
Here,
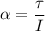
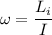
Put the value of angular acceleration and angular velocity
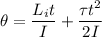
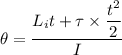
Put the value into the formula
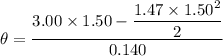
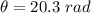
(c). We need to calculate the work done on the wheel
Using formula of work done
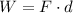
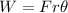
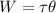
Put the value into the formula
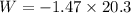
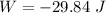
(d). We need to calculate the average power of the flywheel
Using formula of average power
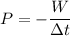
Put the value into the formula
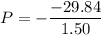
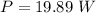
Hence, (a). The magnitude of the average torque acting on the flywheel about its central axis during this period is 1.47 N-m.
(b). The angle that the flywheel does turn is 20.3 rad.
(c). The work done is -29.84 J.
(d). The average power of the flywheel is 19.89 W.