Answer:
Answer: Option d.
Step-by-step explanation:
Accelerated Motion
When an object changes its spped in the same amounts in the same times, the acceleration is constant and its value is
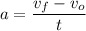
Where
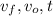 are the final speed, initial speed, and time taken to change them, respectively
are the final speed, initial speed, and time taken to change them, respectively
From the above equation we can know
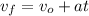
The distance traveled is computed as
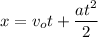
The question talks about a car moving in a straight line with constant acceleration. It goes through the points p,q,r such as
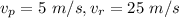
The ratio of the distances traveled in each segment is
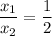
being
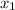 the distance from p to q and
the distance from p to q and
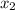 the distance from q to r
the distance from q to r
It means that
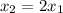
From the equation for speed
![v_q=v_p+at_1\ \ \ ..........[1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/high-school/1u4dfa68eh9667bonv6dy38rv24ik35frp.png)
![v_r=v_q+at_2\ \ \ ..........[2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/high-school/ogh5lo0im9t3s31jbkzr6cnnbg2fr1wwmv.png)
Replacing [1] into [2]
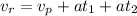
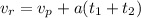
Solving for a
![\displaystyle a=(v_r-v_p)/(t_1+t_2)\ \ \ .........[3]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/high-school/r3p5q4qw80u6l2lie9c2tf85r6b8icnkzo.png)
We now write the equation for both distances .
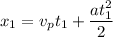
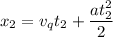
Using [1] again
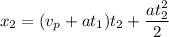
Since
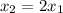
We have
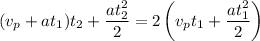
Operating
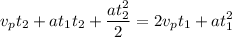
Rearranging
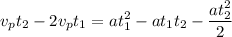
Factoring both sides
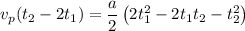
Replacing the equation [3] for a :
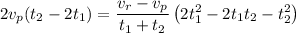
Replacing
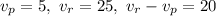 , and operating the denominator
, and operating the denominator
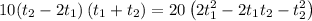
Operating and simplifying, we get a second-degree equation
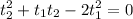
Factoring
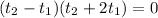
The only positive and valid answer is
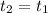
Or equivalently
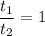
The option d. is correct