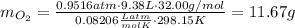Answer:
a. 8.37 g,
b. 11.67 g
Step-by-step explanation:
A) Given:
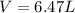
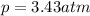
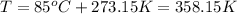
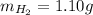
We need to find the mass of argon.
Firstly, we need to apply the ideal gas law in order to find the total number of moles of gases present in the flask:
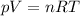
From here:
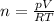
Substituting the variables:
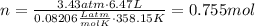
Find the number of moles of hydrogen dividing its mass by the molar mass:
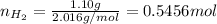
Now find the moles of argon:
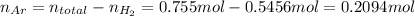
Using the molar mass of argon, convert this number into mass:
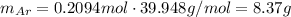
B) Given:
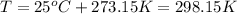
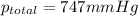
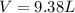
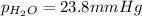
Firstly, the total pressure is equal to the sum of the vapor pressure of water and the partial pressure of oxygen. Knowing this, solve for the pressure of oxygen:
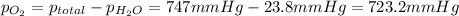
Use the ideal gas law:
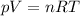
Rearrange the equation, so that we have moles in terms of the mass and the molar mass of oxygen:
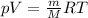
Convert the pressure of oxygen into atm knowing that 1 atm = 760 mm Hg. Then:
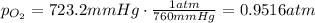
Now rearrange the ideal gas law equation for mass:
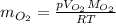
Solve using the variables identified: