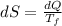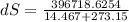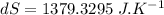Answer:
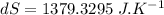
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
- mass of iron,
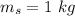
- initial temperature of iron,
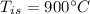
- mass of water,
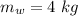
- initial temperature of water,
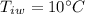
We have,
- Specific heat of iron,
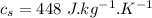
- Specific heat of water,
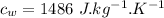
Now the final temperature of the system assuming that no heat is lost to the surrounding:
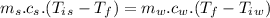
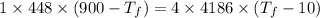
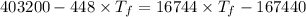
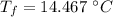
Now the change in heat energy:
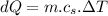
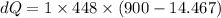
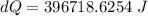
Hence the change in the entropy of the system: