Answer:
E = 18.54 keV
Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction of the tritium beta decay is:
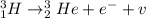 (1)
(1)
To determine the total energy released in the equation (1) we need first write the energy conservation for that equation:
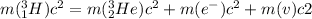 (2)
(2)
From equation (2):
m(v) = 0 and,
m(e⁻) << m(³H) and m(³He), so its mass can be neglected
The energy released in the reaction (1) is:
![E = [m(_(1)^(3) H) - m(_(2)^(3) He)]c^(2) = [3.0160492 u - 3.0160293 u]c^(2) = 0.0000199 uc^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/ghul575bq5155m349t7b5mlyd8n0a4ipl3.png)
Since 1 uc² = 931.4941 MeV, the energy released in reaction (1) in keV is:
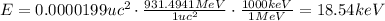
Therefore, the energy released in reaction (1) is 18.54 keV.
I hope it helps you!