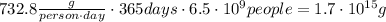Answer:
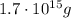
Step-by-step explanation:
Glucose reacts with oxygen do produce carbon dioxide and water:
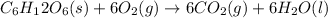
Given a daily mass of glucose:
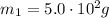
Find moles of glucose:
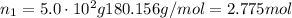
From stoichiometry of this equation, moles of carbon dioxide can be found by multiplying this amount by 6:
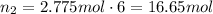
Convert this into mass using the molar mass of carbon dioxide:
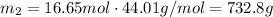
This is the mass of carbon dioxide per person per day. Multiply by the population and by the number of days to get the total mass: