Answer:
d. t distribution with df = 80
Explanation:
Assuming this problem:
Consider independent simple random samples that are taken to test the difference between the means of two populations. The variances of the populations are unknown, but are assumed to be equal. The sample sizes of each population are n1 = 37 and n2 = 45. The appropriate distribution to use is the:
a. t distribution with df = 82.
b. t distribution with df = 81.
c. t distribution with df = 41.
d. t distribution with df = 80
Solution to the problem
When we have two independent samples from two normal distributions with equal variances we are assuming that
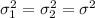
And the statistic is given by this formula:
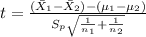
Where t follows a t distribution with
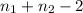 degrees of freedom and the pooled variance
degrees of freedom and the pooled variance
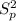 is given by this formula:
is given by this formula:
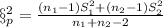
This last one is an unbiased estimator of the common variance
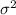
So on this case the degrees of freedom are given by:
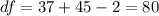
And the best answer is:
d. t distribution with df = 80