Answer:
95.3 N
Step-by-step explanation:
The tension in the cable is found by the equation:
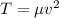
Where
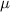 is the mass density, and
is the mass density, and
 is velocity.
is velocity.
First we find mass density:
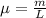 -->
-->
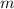 is mass:
is mass:
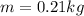 and
and
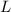 is length of the cable:
is length of the cable:
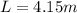 , so:
, so:
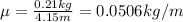
And the velocity:
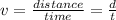
the time is
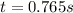 and in that time the pulse went down and back along the cable 4 times, if one time down and back is:
and in that time the pulse went down and back along the cable 4 times, if one time down and back is:
2*4.15m=8.3m,
four times this path is:
4*8.3m=33.2m
thus, the velocity is:
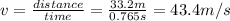
And with this data we can now calculate the tension:
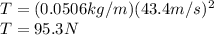
The tension is 95.3N