Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Mass of the dummy, m = 75 kg
Distance, d = 0.8 m
Initial speed of the dummy, u = 0
Final speed of the dummy, v = 11.2 m/s
Firstly finding the acceleration of the test car. Using third equation of motion to find it as :
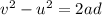
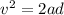
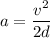
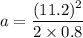
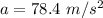
Let F is the average force. It is given by the product of mass and acceleration. It is given by :
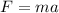
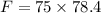
F = 5880 N
Taking ratios,
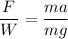
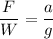
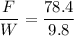
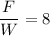
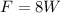
The average force acting on the dummy during the collision is 8 times of his weight. Hence, this is the required solution.