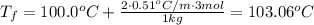Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The normal boiling point of water at 1 atm is
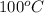 . When a salt is dissolved in a solvent, in this case water, it increases the boiling point of that solvent. The final boiling point can be calculated using the boiling point elevation formula which states that:
. When a salt is dissolved in a solvent, in this case water, it increases the boiling point of that solvent. The final boiling point can be calculated using the boiling point elevation formula which states that:
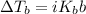
Here:
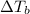 is the change in the boiling point, defined as:
is the change in the boiling point, defined as:
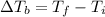
That is, the difference between the final boiling point and the initial boiling point (100 degrees Celsius);
 is known as the van 't Hoff factor, in case we have a non-electrolyte/non-ionic substance, it's equal to 1, however, NaCl (aq) dissociates into 1 mole of sodium and 1 mole of chloride ions, so we have a total of 2 moles of ions per 1 mole of NaCl (aq), meaning i = 2, as the problem states;
is known as the van 't Hoff factor, in case we have a non-electrolyte/non-ionic substance, it's equal to 1, however, NaCl (aq) dissociates into 1 mole of sodium and 1 mole of chloride ions, so we have a total of 2 moles of ions per 1 mole of NaCl (aq), meaning i = 2, as the problem states;
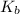 is known as the boiling point elevation constant for the solvent;
is known as the boiling point elevation constant for the solvent;
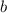 is the molality of substance, which is found dividing moles of solute by the kilograms of solvent:
is the molality of substance, which is found dividing moles of solute by the kilograms of solvent:
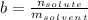
Therefore, we obtain:
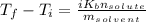
Solving for the final boiling point, add the initial temperature to both sides of the equation:
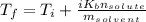
Substitute the given variables: