Answer:
Orbit's semi-major axis length and its period is directly proportional.
Step-by-step explanation:
Orbital period(T) is the time taken for an celestial object to make one complete revolution in the orbit around other object
According to Kepler's laws 3rd of planetary motion stating
The square of an orbital period T of a planet is “directly proportional” to the cube of the "semi-major axis" of its orbit.
The orbital period T is given by
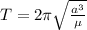
Where
a is the semi-major axis of the orbit
µ = GM which is the standard gravitational parameter
With G is the gravitational constant and M is the mass of body.