Answer:
This is an example of
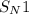 (substitution nucleophilic bimolecular) reaction.
(substitution nucleophilic bimolecular) reaction.
Step-by-step explanation:
Conversion of t-butyl alcohol to t-butyl bromide proceeds through
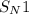 (substitution nucleophilic bimolecular)mechanism.
(substitution nucleophilic bimolecular)mechanism.
In the first step, -OH group in t-butyl alcohol gets protonated.
In the second step, stable tertiary carbocation (t-butyl cation) is produced by removal of
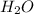 .
.
In the third step, bromide ion attacks to t-butyl cation and produces t-butyl bromide.
Removal of
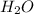 from n-butyl alcohol will produce an unstable primary carbocation (n-butyl cation). Hence, to produce this unstable carboction, large amount of activation energy is required. Therefore, n-butyl alcohol gives much slower reaction with HBr.
from n-butyl alcohol will produce an unstable primary carbocation (n-butyl cation). Hence, to produce this unstable carboction, large amount of activation energy is required. Therefore, n-butyl alcohol gives much slower reaction with HBr.
Reaction mechanism has been shown below.