Answer:
Approximately
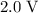 .
.
Approximately
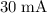 . (assumption: the LED here is an Ohmic resistor.)
. (assumption: the LED here is an Ohmic resistor.)
Step-by-step explanation:
The two resistors here
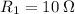 and
and
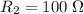 are connected in parallel. Their effective resistance would be equal to
are connected in parallel. Their effective resistance would be equal to
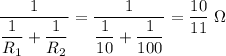 .
.
The current in a serial circuit is supposed to be the same everywhere. In this case, the current through the LED should be
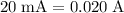 . That should also be the current through the effective
. That should also be the current through the effective
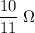 resistor. Make sure all values are in standard units. The voltage drop across that resistor would be
resistor. Make sure all values are in standard units. The voltage drop across that resistor would be
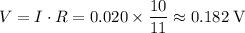 .
.
The voltage drop across the entire circuit would equal to
- the voltage drop across the resistors, plus
- the voltage drop across the LED.
In this case, that value would be equal to
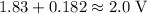 . That's the voltage that needs to be supplied to the circuit to achieve a current of
. That's the voltage that needs to be supplied to the circuit to achieve a current of
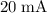 through the LED.
through the LED.
Assuming that the LED is an Ohmic resistor. In other words, assume that its resistance is the same for all currents. Calculate its resistance:
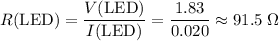 .
.
The resistance of a serial circuit is equal to the resistance of its parts. In this case,
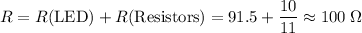 .
.
Again, the current in a serial circuit is the same in all appliances.
 .
.