Para resolver este problema es necesario aplicar los conceptos relacionados a la conductividad térmica, para lo cual se tiene matematicamente que
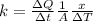
Where,
K = thermal conductivity
A = Cross-sectional Area
 = Change at temperature
= Change at temperature
x = Distance
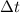 = Difference of time
= Difference of time
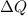 = Heat exchange energy
= Heat exchange energy
Our values are given as follow,
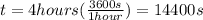
The total heat required to change the phase of ice would be
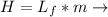 Where Lf Latent heat of fussion and m is the mass.
Where Lf Latent heat of fussion and m is the mass.
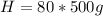
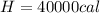
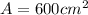
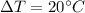
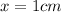
Replacing we would have:
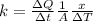
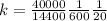
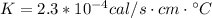
Therefore the correct answer is D.