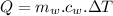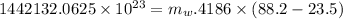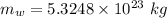Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the given reaction,
heat released by thecombustion of 2 molecules of Methanol,
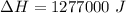
we know that molecular mass of Methanol,
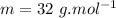
∴12 gram of methanol =
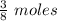
we know 1 mole =
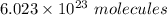
so,
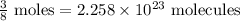
Heat from the combustion of
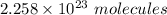 :
:
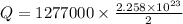
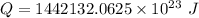
Now the mass of water that can be heated from 23.5°C to 88.2°C :