Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
The equation for the buffer equilibrium is
HA + H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + A⁻
1. Calculate the composition of the original buffer
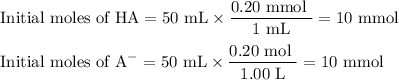
So you have 10 mmol of HA and 10 mmol of A⁻ in 100 mL of the buffer.
2. pH after adding NaOH
(a) Find new composition of the buffer
The base reacts with the HA and forms A⁻
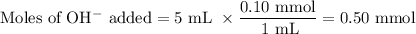
HA + H₂O ⇌ H₃O⁺ + A⁻
I/mmol: 10 10
C/mmol: -0.5 +0.5
E/mmol: 9.5 10.5
(b) Find the new pH
![\begin{array}{rcl}\text{pH} & = & \text{pK}_{\text{a}} + \log \left(\frac{[\text{A}^(-)]}{\text{[HA]}}\right )\\\\& = & 4.7 +\log \left((10.5)/(9.5)\right )\\\\& = & 4.7 + \log1.11 \\& = & 4.7 +0.043\\& = & \mathbf{4.7}\\\end{array}\\\text{The new pH is $\large \boxed{\textbf{4.7}}$}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/jmzs2i694rd9sydffs9rbsupr8bx6jzw3r.png)