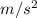Answer:
The magnitude of the resultant acceleration is 2.2
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass (m) of the sailboat = 2000 kg
Force acting on the sailboat due to ocean tide is
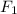 = 3000N
= 3000N
Eastwards means takes place along the positive x direction
Then
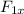 = 3000N and
= 3000N and
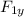 = 0
= 0
Wind Force acting on the Sailboat is
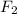 = 6000N directed towards the northwest that means at an angle 45 degree above the negative x axis
= 6000N directed towards the northwest that means at an angle 45 degree above the negative x axis
Then
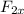 = -(6000N) cos 45 degree = -4242.6 N
= -(6000N) cos 45 degree = -4242.6 N
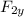 = (6000N) cos 45 degree = 4242.6 N
= (6000N) cos 45 degree = 4242.6 N
Hence , the net force acting on the sailboat in x direction is
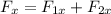
= - 3000 N + 4242.6 N
= - 3000 N +4242.6 N
= 1242.6N
Net Force acting on the sailboat in y direction is
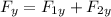
= 0+ 4242.6N
= 4242.6N
The magnitude of the resultant force =
Using pythagorean theorm of 1243 N and 4243 N
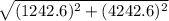
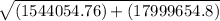
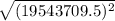
4420.8 N
F = ma
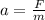
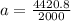
=2.2