Answer:
To select a sample of 27 women with a mean height less than 66 inches is more likely than to randomly select 1 woman with a height less than 66 inches
Explanation:
1) The probability of randomly selecting 1 woman with a height less than 66 inches is
P(z<z(66)) where z(66) is the z-score of the woman whose height is 66 inches.
z score can be calculated using the formula
z(66)=
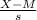 where
where
- M is the mean height of women aged 20-29 (64.9 inches)
- s is the standard deviation (2.3 inches)
Then z(66)=
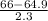 ≈ 0.48
≈ 0.48
and P(z<0.48) = 0.6844
2) The probability of selecting a sample of 27 women with a mean height less than 66 inches can be calculated using the equation
t=
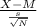 where
where
- M is the average height of women aged 20-29 (64.9 inches)
- s is the standard deviation (2.3 inches)
- N is the sample size (27)
t=
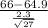 ≈ 2.49
≈ 2.49
looking t-table P(t<2.49)≈0.9903
Since 0.9903>0.6844 we can conclude that to select a sample of 27 women with a mean height less than 66 inches is more likely than to randomly select 1 woman with a height less than 66 inches