Answer:
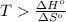
Step-by-step explanation:
The spontaneity of a reaction is described by the Gibbs free energy change. Several statements should be emphasized in the context of this problem:
- the change in Gibbs free energy relates enthalpy, entropy and temperature by the following equation:
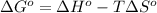 ;
; - if the change in the Gibbs free energy is negative, the reaction is spontaneous, that is:
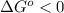 or
or
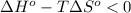 ;
; - if the change in the Gibbs free energy is positive, the reaction is non-spontaneous, that is:
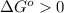 or
or
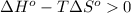 .
.
In this problem, we wish to find the temperature at which the given reaction becomes spontaneous, that is, the minimum T value for which we obtain a negative value of the Gibbs free energy change:
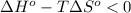
Rearrange the inequality:
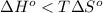
Divide both sides by the change in entropy:
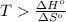
Let's take an example. Let's say that we have a change in enthalpy as 50 kJ/mol and a change in entropy of 100 J/K, then:
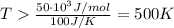
Thus, for these conditions, our reaction would become spontaneous at 500 K and above.