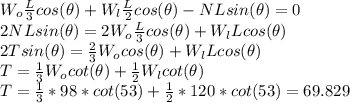Answer:
68.829 N
Step-by-step explanation:
The given parameters are:
Weight of ladder,
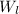 = 120 N
= 120 N
Weight of object,
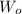 = 98 N
= 98 N
Angle,
 = 53°
= 53°
And we also know that, while
Length of ladder = L
Distance the object is placed = L/3
If we apply translational equilibrium horizontally, then
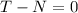 , so
, so
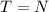
If we apply rotational equilibrium about the distance the object is placed, then