Answer:
It results -14 in either way
Explanation:
Velocity As A Rate Of Change
The velocity of an object can be computed as the rate of change of its displacement (or position taken as a vector) over time. If we compute it as a derivative, it's called instantaneous velocity, and if computed as the slope of the function (difference quotient) at a certain point it's the average velocity
The position of the object as a function of time is
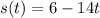
Computing the derivative
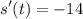
We can see it's a constant value. If we use the slope or rate of change:
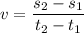
Now let's fix two values for time
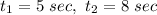
and compute the corresponding positions, by using the given function
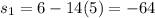
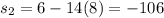
Now we compute the average velocity
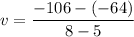
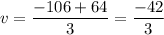
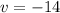
We get the very same result in both ways to compute v. It happens because the position is related with time as a linear function, it's called a constant velocity motion.