Answer : The value of equilibrium constant K at 298 K is, 56.59
Explanation :
The given chemical reaction are:
(1)
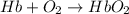 ;
;
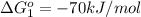
(2)
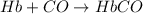 ;
;
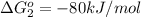
First we have to determine the standard free-energy change for the following reaction.
(3)
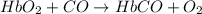 ;
;
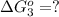
Now we are reversing the reaction 1 and then adding reaction 1 and 2, we get:
(1)
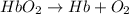 ;
;
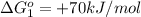
(2)
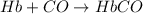 ;
;
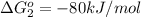
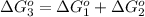
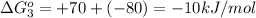
Now we have to calculate the equilibrium constant K at 298 K.
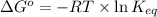
where,
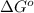 = standard Gibbs free energy = -10kJ/mol = -10000 J/mol
= standard Gibbs free energy = -10kJ/mol = -10000 J/mol
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/K.mol
T = temperature = 298 K
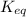 = equilibrium constant = ?
= equilibrium constant = ?
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
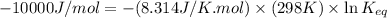
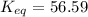
Therefore, the value of equilibrium constant K at 298 K is, 56.59