Answer:
The equilibrium concentration are :
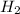 = 0.04 M
= 0.04 M
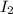 = 0.04 M
= 0.04 M
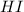 = 0.16 M
= 0.16 M
Step-by-step explanation:
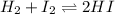
it means 1 mole of iodine and hydrogen produce 2 mole of HI
Concentration(C) : Moles per unit volume.It is expressed in Molarity
(M=mol/L )
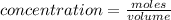
Initial moles :
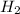 = 1.00
= 1.00
So,
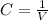
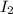 = 1.00
= 1.00
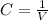
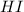 = 0
= 0
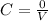
let during the reaction x moles of both
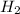 and
and
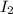 get dissociated , then
get dissociated , then
At equilibrium ,
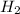 = 1.00 - x
= 1.00 - x
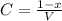
For iodine
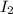 = 1.00 - x
= 1.00 - x
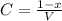
1.00 - x mole of hydrogen will produce 2x of HI
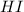 = 2x
= 2x
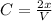
![K_(eq) = ([products]^(coefficient))/([reactants]^(coefficient))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/8uqece93mheg044d6fb0yowxiyor5zo8xd.png)
On solving for x , (look at the image)
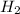 = 0.04 M
= 0.04 M
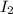 = 0.04 M
= 0.04 M
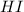 = 0.16 M
= 0.16 M