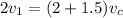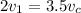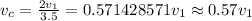Answer:
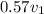
Step-by-step explanation:
From the law of conservation of momentum, the sum of initial momentum equals the sum of final momentum
Momentum, p=mv where m is the mass and v is the velocity
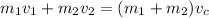 where
where
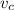 is the common velocity,
is the common velocity,
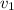 and
and
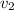 are velocities of 2 Kg moving mass and motionless 1.5 kg mass respectively,
are velocities of 2 Kg moving mass and motionless 1.5 kg mass respectively,
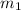 and
and
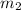 are masses of 2 Kg moving mass and motionless 1.5 kg mass .
are masses of 2 Kg moving mass and motionless 1.5 kg mass .
Since the 1.5 Kg mass is motionless, it's velocity is zero hence
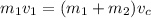
By substitution