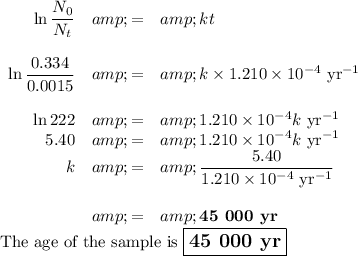Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
Two important equations in radioactive decay are
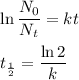
We use them for carbon dating.
(a) Initial activity = 0.23 Bq
(i) Calculate the rate constant
The half-life of ¹⁴C is 5730 yr.
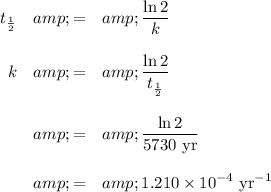
(ii) Calculate the age of the sample
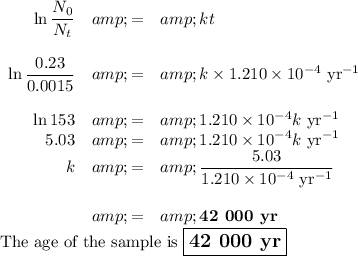
(b) Initial activity = 45 % larger
N₀ = 1.45 × 0.230 Bq = 0.334 Bq