Answer:
Option E.
Step-by-step explanation:
The partition coefficient (D) relates the solute partitioning between two phases, in which the solute extraction from an aqueous phase into an organic phase is represented by:
S(aq) ⇄ S(or)
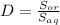 (1)
(1)
When the pH of an aqueous phase increases by the use of an alkaline solution like NaOH, the solubility of a weak acid, for example, acetic acid, increases in the aqueous phase by the following reaction:
CH₃COOH + NaOH ⇄ CH₃COO⁻Na⁺ + H₂O (2)
Therefore, as the pH of the aqueous phase increase, the percent of the weak acid in the aqueous phase increases as a result of acid neutralization (equation 2).
The increase of the weak acid percentage in the aqueous solution produces a decrease in the partition coefficient, since the inverse relationship between the coefficient partition and the solubility in the aqueous phase (equation 1).
So, the correct answer is option E: as the pH increases the value of D decreases and the percentage weak acid left in the aqueous phase increases.
I hope it helps you!