Answer:
51.54°C the final temperature of the calorimeter contents.
Step-by-step explanation:
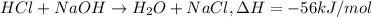
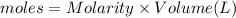
Molarity of HCl= 0.50 M
Volume of HCl= 150.0 mL = 0.150 L
Moles of HCl= n
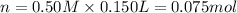
Molarity of NaOH= 1.00 M
Volume of NaOH= 50.0 mL = 0.050 L
Moles of NaOH= n'
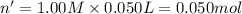
Since moles of NaOH are less than than moles of HCl. so energy release will be for neutralization of 0.050 moles of naOH by 0.050 moles of HCl.
n = 0.050
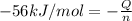
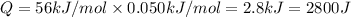
(1 kJ= 1000 J)
The energy change released during the reaction = 2800 J
Volume of solution = 150.0 mL + 50.0 mL = 200.0 mL
Density of the solution (water) = 1.00g/mL
Mass of the solution , m= 200 mL × 1.00 g/mL = 200 g
Now , calculate the final temperature by the solution from :
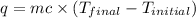
where,
q = heat gained = 2800 J
c = specific heat of solution =
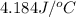
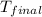 = final temperature =
= final temperature =

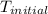 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
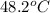
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
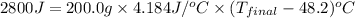
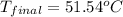
51.54°C the final temperature of the calorimeter contents.