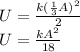Answer:
a)
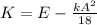
b)
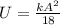
Step-by-step explanation:
The law of conservation of mechanical energy states that total mechanical energy remains constant during oscillation. Mechanical energy is defined as the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy:
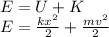
a) The position is one-third the amplitude. So, we have
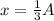 . Replacing and solving for K
. Replacing and solving for K
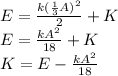
b) The potential energy is defined as:
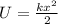
Replacing: